Transgenic Mice Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein under the Control of the Melanocortin-4 Receptor Promoter
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 28 junho 2024

The melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4-R) is an important regulator of energy homeostasis, and evidence suggests that MC4-R-expressing neurons are downstream targets of leptin action. MC4-Rs are broadly expressed in the CNS, and the distribution of MC4-R mRNA has been analyzed most extensively in the rat. However, relatively little is known concerning chemical profiles of MC4-R-expressing neurons. The extent to which central melanocortins act presynaptically or postsynaptically on MC4-Rs is also unknown. To address these issues, we have generated a transgenic mouse line expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the control of the MC4-R promoter, using a modified bacterial artificial chromosome. We have confirmed that the CNS distribution of GFP-producing cells is identical to that of MC4-R mRNA in wild-type mice and that nearly all GFP-producing cells coexpress MC4-R mRNA. For example, cells coexpressing GFP and MC4-R mRNA were distributed in the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus (PVH) and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV). MC4-R promotor-driven GFP expression was found in PVH cells producing thyrotropin-releasing hormone and in cholinergic DMV cells. Finally, we have observed that a synthetic MC3/4-R agonist, MT-II, depolarizes some GFP-expressing cells, suggesting that MC4-Rs function postsynaptically in some instances and may function presynaptically in others. These studies extend our knowledge of the distribution and function of the MC4-R. The transgenic mouse line should be useful for future studies on the role of melanocortin signaling in regulating feeding behavior and autonomic homeostasis.
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

The stimulatory G protein Gsα is required in melanocortin 4

Journal of Comparative Neurology Systems Neuroscience Journal
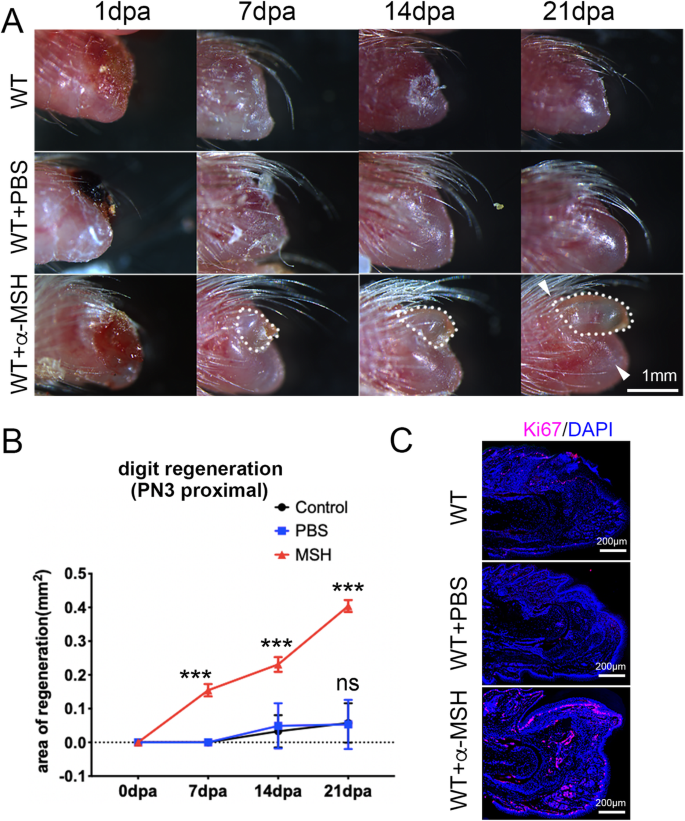
Activation of the Melanocortin-4 receptor signaling by α-MSH

Divergence of Melanocortin Pathways in the Control of Food Intake

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Transgenic Mice Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein under the

Melanocortin-4 Receptor Regulates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity
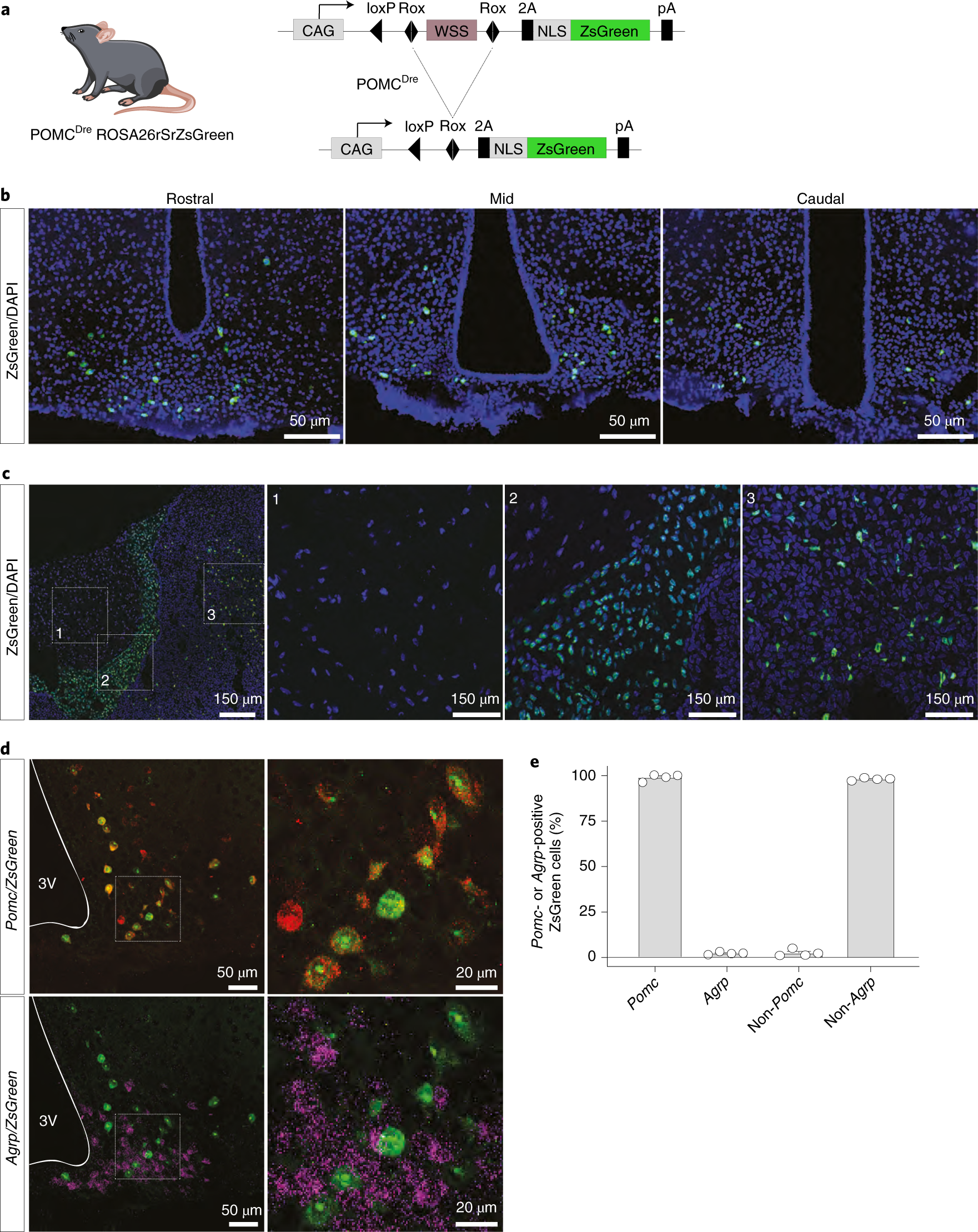
Functionally distinct POMC-expressing neuron subpopulations in

Transgenic Mice Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein under the

Activation of the Melanocortin-4 receptor signaling by α-MSH

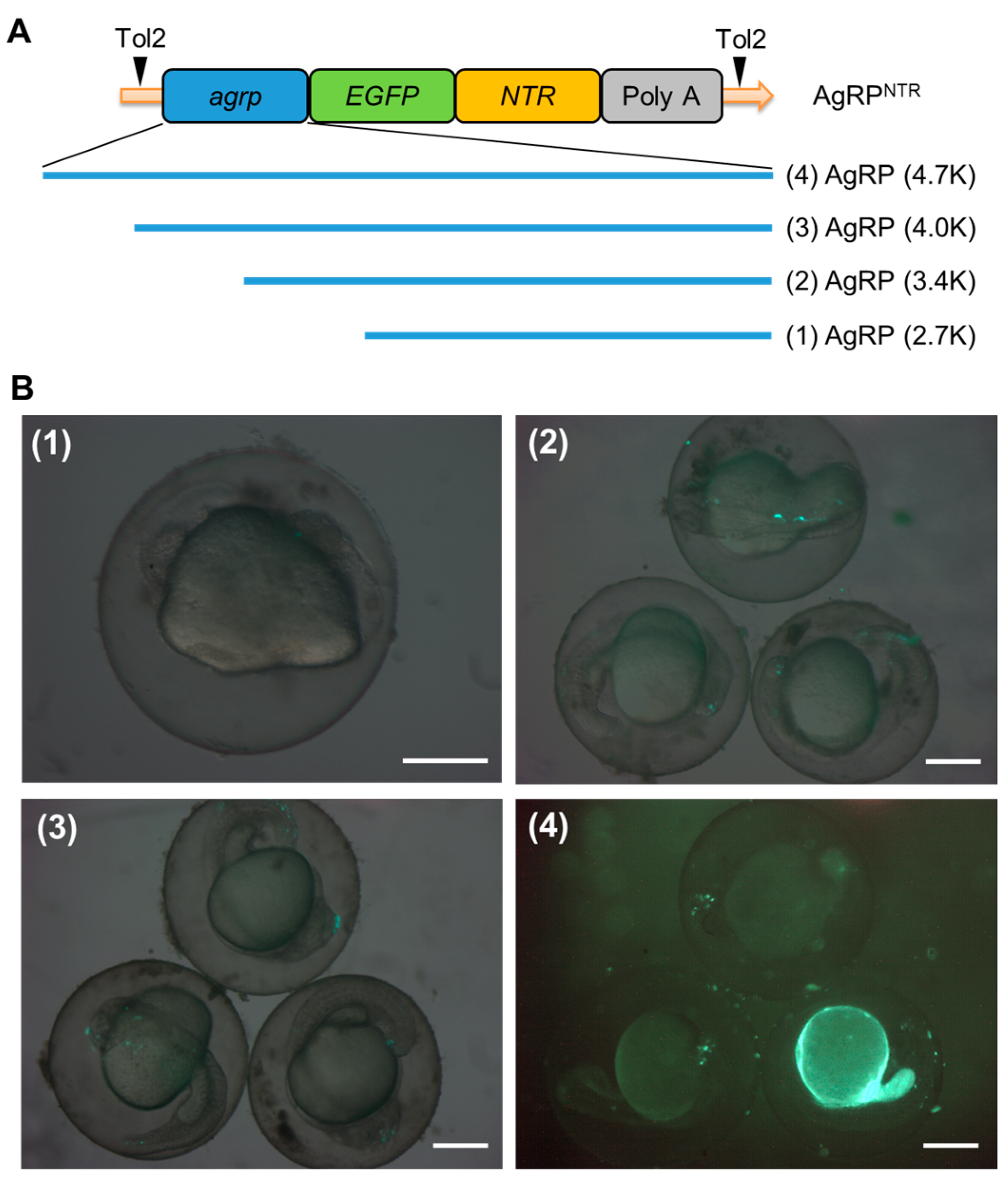
AgRP neuronal expression of GFP directed by 1-kb AgRP promoter in

Journal of Comparative Neurology Systems Neuroscience Journal
Recomendado para você
-
 SCP-7143-J, the crude cookie, AKA Cookie Cosplay : r/SCP28 junho 2024
SCP-7143-J, the crude cookie, AKA Cookie Cosplay : r/SCP28 junho 2024 -
 US20120297504A1 - Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides and methods of using same for increasing plant yield, biomass, growth rate, vigor, oil content, abiotic stress tolerance of plants and nitrogen use efficiency - Google Patents28 junho 2024
US20120297504A1 - Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides and methods of using same for increasing plant yield, biomass, growth rate, vigor, oil content, abiotic stress tolerance of plants and nitrogen use efficiency - Google Patents28 junho 2024 -
 Pride month logo, SCP Foundation28 junho 2024
Pride month logo, SCP Foundation28 junho 2024 -
 An alternative application for reuse of leaching residues: Determination of adsorption behaviour for methylene blue and process optimization - ScienceDirect28 junho 2024
An alternative application for reuse of leaching residues: Determination of adsorption behaviour for methylene blue and process optimization - ScienceDirect28 junho 2024 -
 watched rick and morty thought of this SCP - Imgflip28 junho 2024
watched rick and morty thought of this SCP - Imgflip28 junho 2024 -
 SCP-5417-J: The Deadly Nackle28 junho 2024
SCP-5417-J: The Deadly Nackle28 junho 2024 -
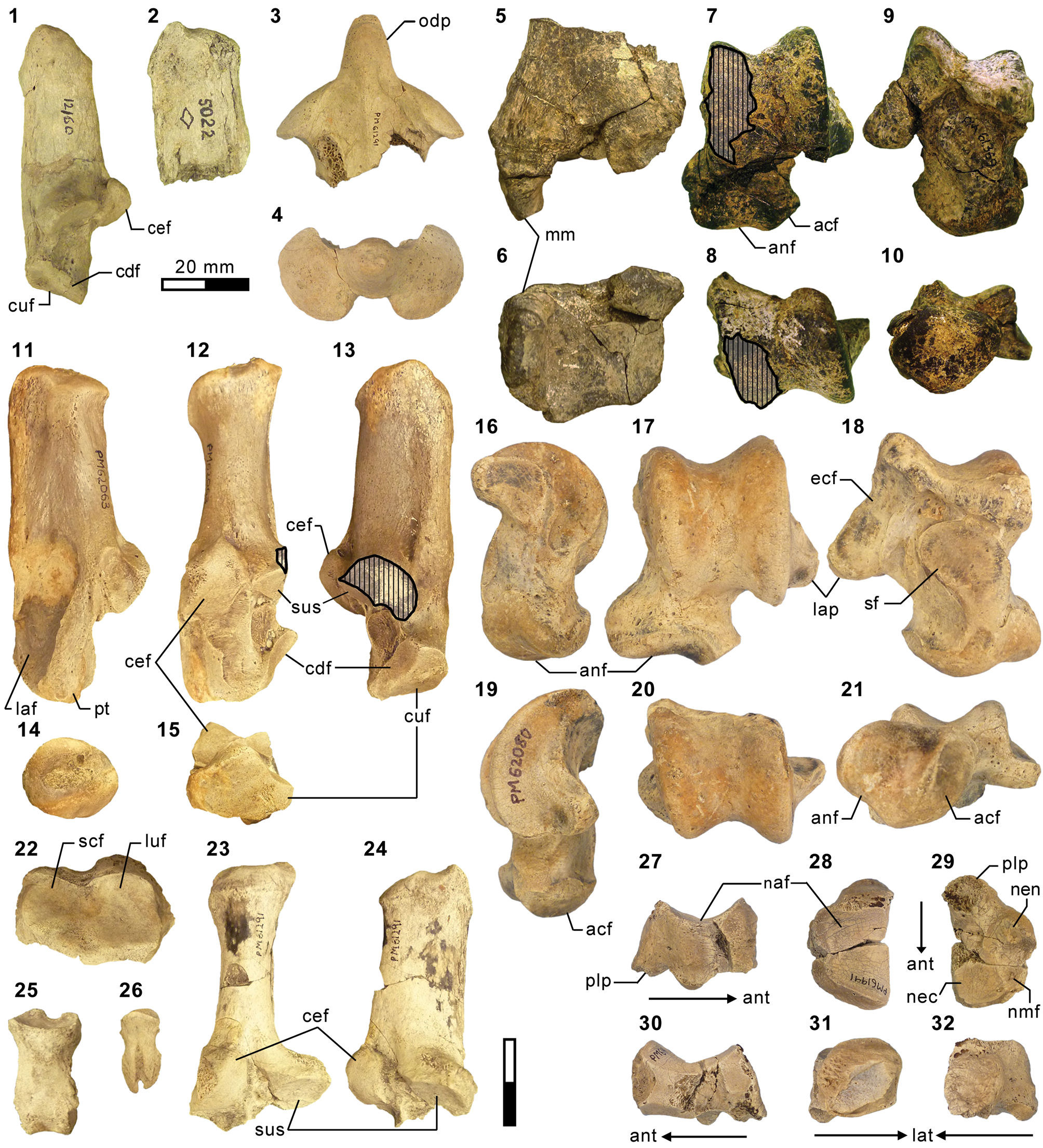 Carnivorous mammals from the middle Eocene Washakie Formation, Wyoming, USA, and their diversity trajectory in a post-warming world, Journal of Paleontology28 junho 2024
Carnivorous mammals from the middle Eocene Washakie Formation, Wyoming, USA, and their diversity trajectory in a post-warming world, Journal of Paleontology28 junho 2024 -
what scp has the most rizz - Brick Hill28 junho 2024
-
 Surprised no one has posted this yet Source(NSFW): - #177353993 added by nuclearnacho at Almost there28 junho 2024
Surprised no one has posted this yet Source(NSFW): - #177353993 added by nuclearnacho at Almost there28 junho 2024 -
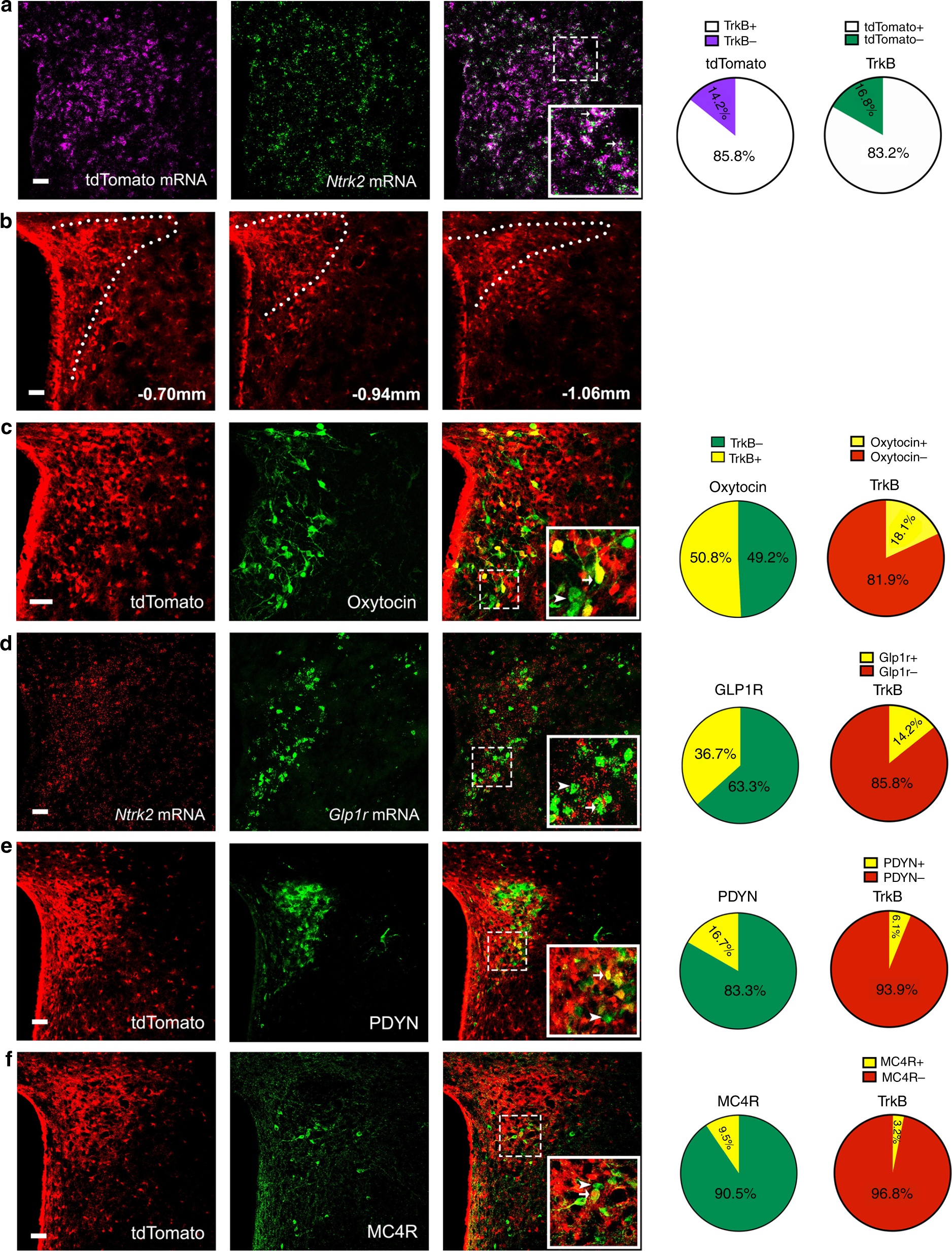 TrkB-expressing paraventricular hypothalamic neurons suppress appetite through multiple neurocircuits28 junho 2024
TrkB-expressing paraventricular hypothalamic neurons suppress appetite through multiple neurocircuits28 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 50 Atividades com Quebra-Cabeça para Imprimir - Online Cursos Gratuitos28 junho 2024
50 Atividades com Quebra-Cabeça para Imprimir - Online Cursos Gratuitos28 junho 2024 -
Mobile - Sonic Dash - Sonic Movie Event Graphics - The Spriters Resource28 junho 2024
-
 Uncharted (2022)28 junho 2024
Uncharted (2022)28 junho 2024 -
 Nissan Super Girl Surf Pro powered by Celsius // 2022 Highlights // Oceanside, CA28 junho 2024
Nissan Super Girl Surf Pro powered by Celsius // 2022 Highlights // Oceanside, CA28 junho 2024 -
 COMO CONSEGUIR LA ESPADA DE RENGOKU!!ROBLOX: BLOX FRUITS GUIA28 junho 2024
COMO CONSEGUIR LA ESPADA DE RENGOKU!!ROBLOX: BLOX FRUITS GUIA28 junho 2024 -
 Levante vs Racing Club de Ferrol - 2023-10-1628 junho 2024
Levante vs Racing Club de Ferrol - 2023-10-1628 junho 2024 -
 O quiz do PSGFlipar – Diversão e informação em um flip28 junho 2024
O quiz do PSGFlipar – Diversão e informação em um flip28 junho 2024 -
 Elizabeth, Hawk & Meliodas, Nanatsu no Taizai/The Seven Deadly Sins28 junho 2024
Elizabeth, Hawk & Meliodas, Nanatsu no Taizai/The Seven Deadly Sins28 junho 2024 -
 Fnaf 4 Characters Canon by aidenmoonstudios on DeviantArt28 junho 2024
Fnaf 4 Characters Canon by aidenmoonstudios on DeviantArt28 junho 2024 -
 UGC Program: Updates to avatar bodies and heads + opening up creation - Announcements - Developer Forum28 junho 2024
UGC Program: Updates to avatar bodies and heads + opening up creation - Announcements - Developer Forum28 junho 2024